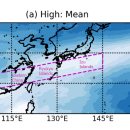
Macroscopic characteristics of the diurnal variation of clouds associated with the Baiu–Meiyu rainband using cloud property data estimated from Himawari-8 infrared measurement
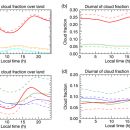
Diurnal variation of clouds and precipitation associated with the Baiu–Meiyu rainband, which characterizes the climate in East Asia, is apparent and has regional characteristics. However, diurnal variation of optically-thin high clouds, as seen from mature stage to dissipating stage in the life cycle of convective clouds, has not been well understood. Our group attempted to clarify the macroscopic characteristics of …
Retrieval of cloud properties from spectral zenith radiances observed by sky radiometers
Though satellite observations are vital in understanding cloud characteristics and the roles of clouds on climate system, the quality assurance of cloud properties observed by satellites is recognized as one of the important tasks in cloud remote sensing community. Cloud observation from surface is useful in validating such satellite cloud products as well as understanding cloud characteristics in more detail …
Wintertime modulation of the local cloud and diagnostic fields by the hadley cell subsiding boundary over the Western North Pacific
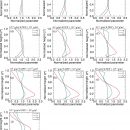
Over the winter western North Pacific, the descending branch of the Hadley cell locates climatologically around 35˚N, while recently, it has been proved to shift poleward since the late 1970s. Correspondingly, the regional climate would be modulated by the migration of this subsiding zone. In our recent study, we examined the responses of the clouds, the cloud radiative effects, and …
Development of a ground-based cloud observation technique using the deep learning
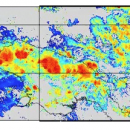
Observation of the spatial distribution of cloud optical thickness (COT) is useful for the prediction and diagnosis of photovoltaic power generation. However, optical remote sensing of cloud is difficult because the three-dimensional (3D) radiative transfer effects should be taken into account. We propose a method to train a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) based on a 3D radiative transfer model, …
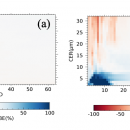
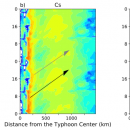
Characteristics of diurnal pulses observed in Typhoon using retrieved cloud property data
We have analyzed a typhoon in high temporal and spatial resolution by using the cloud properties from Japanese geostationary satellite Himawari-8 (Wang et al., 2019), whose retrieval method had been developed in our group. By dividing the high clouds into three COT categories: opaque high cloud (OHC), cirrostratus (Cs), and cirrus (Ci). Two alternatively appeared peaks in the cloud top …
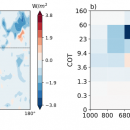
Development of a Rapid Retrieval Method for Cloud Optical Thickness and Cloud-Top Height Using Himawari-8 Infrared Measurements
We have developed a method for retrieval of cloud optical thickness and cloud-top height from measurements of the two infrared bands of Himawari-8 (Sakai et al., 2019). The method is based on an empirical, simple model of brightness temperatures of Himawari-8 as functions of cloud optical thickness, cloud-top height, satellite zenith angle, surface temperature, and water vapor column amount. By …
Study of ice cloud vertical inhomogeneity and its impacts on cloud retrieval using thermal infrared measurements
Despite the vertically inhomogeneous (VIH) structure of ice clouds, current passive remote sensing methods assume plane‐parallel homogeneous (PPH) layers, which can lead to retrieval errors. An adequate VIH cloud model is required to improve retrieval performance. We analyzed CloudSat and CALIPSO satellite measurements of 1‐year period to model cloud vertical inhomogeneity; then studied the impacts of cloud vertical inhomogeneity on …
Cloud property retrieval from multiband infrared measurements by Himawari-8
We have developed an algorithm for retrieving the cloud properties from thermal infrared measurements by the Japanese new-generation geostationary satellite, Himawari-8 (Iwabuchi et al., 2018). The Himawari-8 has significantly improved observation capabilities with 16 bands in visible-to-infrared spectrum and high temporal and spatial resolutions. With the help of high frequency of observations (10-minunte interval), we investigates tropical cloud evolution …