Remote Sensing of Inhomogeneous Clouds Using Deep Learning: A feasibility study
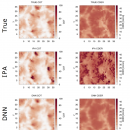
We have developed a new method to estimate the cloud physical properties from multispectral, multipixel measurement data from satellite using the deep learning (Okamura, Iwabuchi, Schmidt, 2017). It is the first study (to our best knowledge) using the deep learning for atmospheric remote sensing. In this study, we have developed deep learning models that use solar reflectance image data …
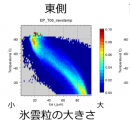
CloudSat · CALIPSO elucidation of difference in vertical distribution of cloud microphysical quantity in western and eastern part of tropical Pacific using satellite data
While the western side of the tropical Pacific (around the Indonesian islands) is a region with high sea surface temperature in the world, the eastern side (the continental side of South America) is influenced by rising cold water off the coast of Peru, so the sea surface temperature is lower relative to the west side. It is known that the …
Revealing the Twilight Sky Color by Photographic Observations and Theoretical Calculation
A Master-course student in our laboratory, Masanori Saito, has studied the effects of tropospheric aerosol on twilight sky color based on photographic observations and theoretical calculations. The result has been published in a paper in peer-review journal, SOLA (Scientific Online Letters on the Atmosphere), by him and co-authors on Feb. 28, 2013. The twilight sky is one of the most …
Development of 3D radiative transfer models
Clouds have complex structures even at very small spatial scale, varying second by second (Fig. 1). The small-scale variability of cloud influences radiative transfer and radiation observed from satellites. However, numerical models cannot treat the variability at infinitesimal scale, so idealized cloud morphology should be used. Fig. 1. A photo of fair weather cumulus. Our group is developing 3D radiative …
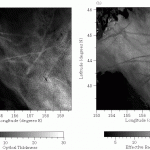
Observation of ship track from space: How does cloud change by human activity?
An increase of anthropogenic aerosols from air pollution and biomass burning may change the distribution of cloud and precipitation and influence global and regional climate. Several types of aerosol particles can act as cloud condensation nuclei and increase the number of cloud particles, and mean particles size decreases, increasing the cloud reflectivity. Also, it is suggested that the aerosols may …